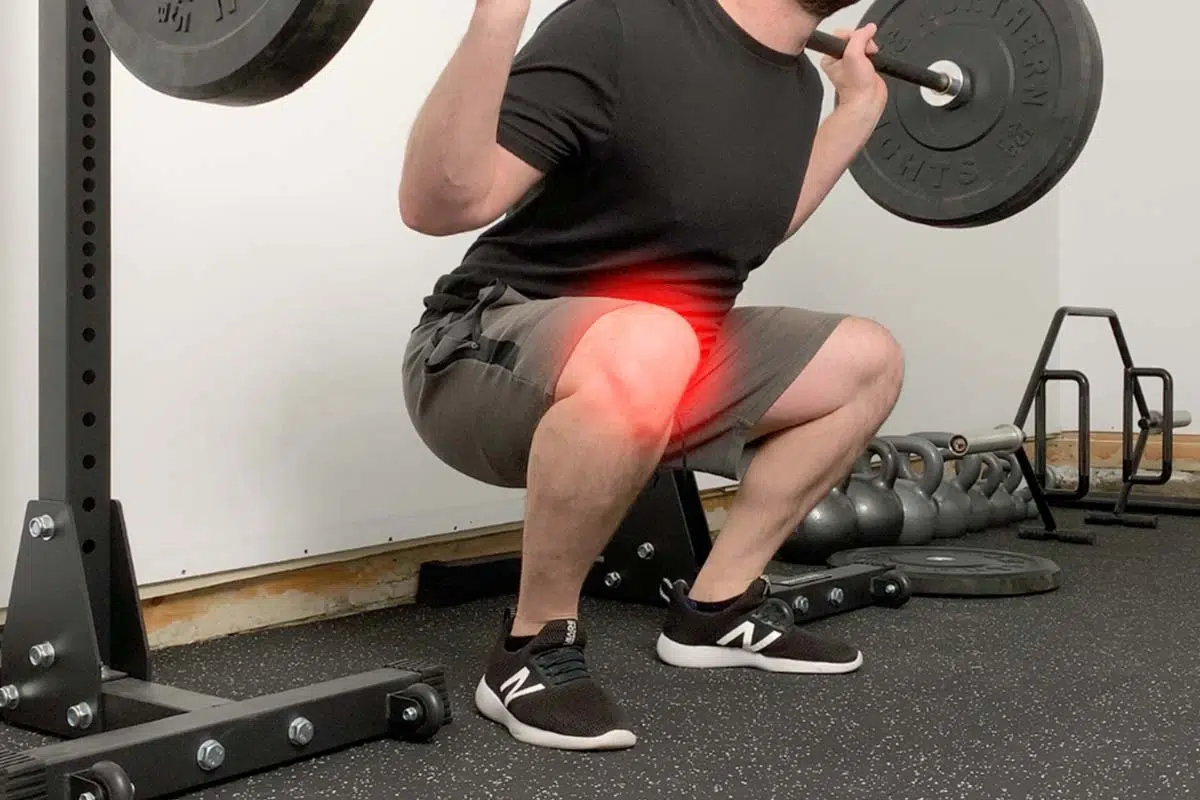
Knee swelling and pain can result from injuries and arthritis. Certain causes can be managed at home, whereas others necessitate medical intervention. Different factors cause knee pain. Being overweight increases knee problems. Knee pain can result from overuse. A history of arthritis can cause knee pain.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Following are the causes of knee pain:
- Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus arthritis, and gout are classifications of arthritis.
- Baker’s cyst—A fluid-filled swelling behind the knee that may be caused by arthritis or other inflammation.
- Cancers that start or spread to bones
- Oswestry disease
- Knee-bone infection
- Knee infection
- Bursitis—knee inflammation from prolonged kneeling, overuse, or injury.
- Inflammation of the tendon with activity change can be caused by overuse or deconditioning.
- Kneecap dislocation
- Kneecap or bone fracture
- A thick band from your hip to the outside of your knee can be injured.
- PFO syndrome—front knee pain around the kneecap
- Ligament tear. An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury can cause knee bleeding, swelling, or instability.
- Torn meniscus cartilage—knee joint pain inside or out
- Strain or sprain—minor ligament injuries from sudden or unnatural twisting
Causes of Acute Knee Swelling
Possible causes of acute knee swelling:
Bursitis
Inflammation of the knee’s bursae causes bursitis. An inflammatory knee response causes swelling. Swelling presses on other knee parts and causes pain. Common bursitis causes include frequent kneeling or blunt force trauma to the knee, according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The knee is examined, and an X-ray or MRI may be ordered to diagnose this. Treatment for bursitis may include compression, ice packs, knee elevation, rest, and NSAIDs like ibuprofen for pain relief.
Arthritis
Knee swelling is also common due to arthritis. Chronic inflammation underlies arthritis, but the five key markers of acute inflammation may still be present. Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, causes knee swelling by breaking down cartilage in the knee, according to the Arthritis Foundation. Rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammatory form where the immune system attacks joints. Juvenile arthritis occurs in individuals under 16 years old; reactive arthritis is a chronic type that often follows genital or urinary tract infections; infectious arthritis is caused by joint swelling; and gout is caused by uric acid buildup in the blood. Before diagnosing arthritis, doctors will ask about other symptoms and medical history. They may also suggest blood tests and X-rays.
The best arthritis treatment depends on the type and may include:
- Use pain relief medication like NSAIDs
- Make lifestyle changes like exercise and physical therapy.
Acute Injuries
Acute knee injuries can result from sports, exercise, or blunt force trauma. Common acute knee injuries include:
- Sprains from sudden twists or hits
- Tendonitis from overuse or joint damage
- Torn cartilage from trauma
Doctors may use X-rays, CTs, or MRIs to assess damage. Treatment alternatives may encompass rest, utilization of braces or assistive devices, administration of NSAIDs, physical or occupational therapy, and surgical intervention.
Infections
The following infections can cause knee swelling:
- lupus, a chronic immune system disorder that attacks healthy tissues, including joints
- Lyme disease, spread by ticks, causes flu-like symptoms, a rash, and joint swelling.
Testing can help doctors determine if swelling is caused by an infection. They may prescribe antibiotics for Lyme disease or other bacterial infections.
Care at Home for Knee Swelling and Pain
Simple knee pain causes usually resolve on their own while you treat them. Contact your knee pain doctor in Dallas if an accident or injury causes knee pain.
- To alleviate mild knee pain, rest and refrain from activities that exacerbate it. Do not apply weight to your knee.
- Apply ice, attempt it hourly for a duration of 15 minutes. Administer a minimum of four applications daily following the initial day.
- Cover your knee with a towel before icing. Avoid sleep while using ice. Leave it on too long and get frostbite.
- Keep your knee elevated to reduce swelling.
- Elastic bandages and sleeves are available at most pharmacies. This may support and reduce swelling.
- Take Motrin or Aleve for pain and swelling. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) relieves pain but not swelling. If you have medical issues or have taken these drugs for more than a day or two, consult your pain management in fort worth.
- Place a pillow beneath or between your knees.
- Home remedies for knee swelling include elevating the affected leg, massaging the leg and knee, resting an ice pack against the knee for 15-20 minutes, strengthening supporting muscles, using a band or compression sleeve, and taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications.
General Knee Pain Relief and Prevention Tips
Engage in warm-up and cool-down activities prior to and following exercise.
- Stretch your quadriceps and hamstrings.
- Walk down hills instead of running.
- Swim or bike instead of running.
- Cut back on exercise.
- Avoid cement and pavement by running on a track.
- Overweight? Lose weight. When climbing stairs, every pound (0.5 kilogram) of overweight puts 5 pounds (2.25 kilograms) of pressure on your kneecap. Jumping adds more pressure. Ask your doctor about weight loss.
- Try orthotics and shoe inserts for flat feet.
- Make sure your running shoes fit, cushion, and are well made.
- Where your knee pain is coming from may determine your next steps.
Summary
Knee swelling and pain can result from arthritis, infection, or injury. NSAIDs and ice packs can reduce swelling at home. If a person suspects an underlying condition causes swelling, they should seek medical attention. Doctors can diagnose and treat damage with imaging and antibiotics.